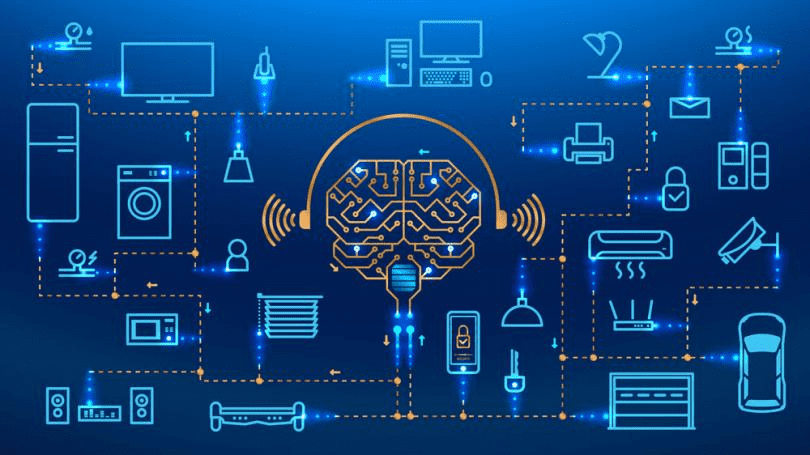
What is IoT?
IoT, internet of things, refers to the billions of physical devices that are connected to each other via the internet and sharing data and other information. Thanks to the arrival of affordable computer chips and the commonality of wireless networks, it is more simple than ever to turn anything into a part of the IoT. By connecting these devices together, adding sensors and writing software to read and manipulate data, these devices are now becoming smarter than ever and are adding an aspect of digital intelligence to our daily lives.
Examples of IoT
As IoT continues to grow, its products are becoming more prevalent than ever in a society. One of the most popular IoT implementations is smart homes. Smart Home appliances are one of the most affordable and valuable IoT products on the market as the devices communicate with one another to create a smooth flow of data transmission. Some of the most common appliances are Amazon Alexa, Nest thermostat, and much more! Other common examples of IoT include smartwatches, temperature sensors, GPS trackers, and smart doorbells.
Why IoT Matters
In IoT, devices are connected to the internet where they are equipped with the capabilities to collect, send, and receive data. From a consumer point of view, IoT devices increase the efficiency of tasks and are able to perform them autonomously.
Let’s take a smart doorbell for example. Smart doorbells allow you to monitor the activity near the front of your house, be it a guest, mail package, or even a thief. By replacing the peephole on common doors, smart doorbells are able to act on its own and notify users when activity is noticed outside their front door by streaming video to the user’s mobile devices. Not only does this alleviate the burden of checking your front door but also ensures the user’s safety by enabling them to view and communicate to those outside their home.
To be rendered as “smart”, a device doesn’t need to have a powerful brain of its own, all it requires is to be connected to a more powerful machine. A connection is the principle of the IoT.
In the Internet of Things, a connection is used for 2 primary purposes:
- To collect and send data
- To receive and act on data
All of these fundamentals are vital to building a rudimentary IoT device.
Collecting and Sending Information
The collection of data is performed through the use of sensors. Sensors are distributed in various forms: motion sensors, pressure sensors, temperature sensors, air quality sensors, and so on. When connected to the internet, these senors are automatically able to collect the data we need and upon request, send the data over the internet to servers or to other IoT devices.
Receiving and Responding to Information
Upon receiving information from sensors, the information is either kept static for analytical/display purposes or is manipulated to derive further information.
In our day to day lives, we are often blind to the occurrences of data manipulation. For example, your printer receives a document sent by your laptop/mobile device and prints it out. Your car key, when “unlock” is pressed, sends a signal to your car which unlocks the door.
What’s Next?
The potential of the IoT is endless and as Bruce Schneier says,
“The internet is no longer a web that we connect to. Instead, it’s a computerized, networked, and interconnected world that we live in. This is the future, and what we’re calling the Internet of Things.”
If you are interested in learning more about the IoT and building IoT projects of your own, you’ve come to the right place! Stay tuned to our blogs as we will be posting more articles and tutorials on how you can kickstart your journey into the Internet of Things.